Climate change has emerged as one of the most pressing challenges of our time. As global temperatures continue to rise, cities around the world are facing increasingly severe climate-related hazards, such as floods, storms, heatwaves, and rising sea levels. Building resilient cities has become an urgent priority for urban planners, architects, and engineers. This blog will explore the concept of resilient cities and discuss some of the most innovative climate-adaptive construction techniques that are helping to protect urban environments and their inhabitants from the impacts of climate change.
What is a Resilient City?
A resilient city is one that can withstand and recover from the impacts of climate change, natural disasters, and other stressors. Resilience is not only about preparing for and coping with extreme events, but also about adapting and transforming urban systems in response to long-term changes in climate and environmental conditions. Building resilient cities involves a wide range of strategies, from improving infrastructure and building design to fostering social cohesion and strengthening local economies.

Climate-Adaptive Construction Techniques
The construction sector plays a critical role in shaping the resilience of cities. By adopting innovative climate-adaptive construction techniques, we can create buildings and infrastructure that are better equipped to withstand the impacts of climate change. Some of the most promising techniques include:
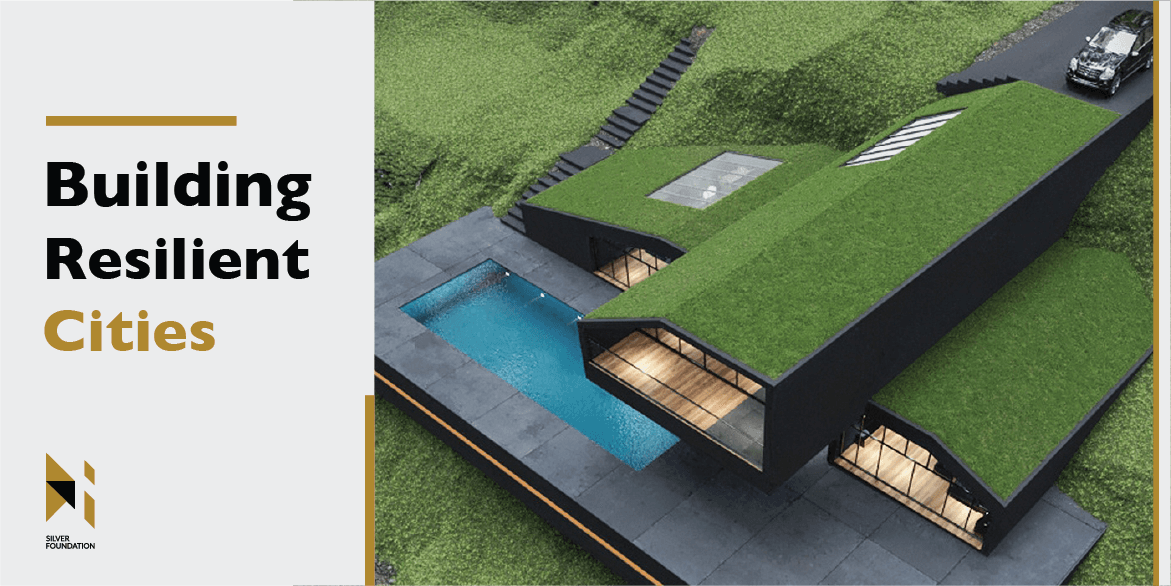
Green Roofs and Walls
Green roofs and walls are covered with vegetation, which helps to reduce heat absorption, improve air quality, and manage storm water runoff. By acting as insulation, green roofs keep buildings cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter, reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Green walls can also provide a natural barrier against heat and noise pollution, improving the comfort and well-being of building occupants.
Flood-Resistant Design
Flood-resistant design involves building structures that can withstand and recover quickly from flooding events. This can include elevating buildings above anticipated flood levels, installing watertight doors and windows, and using materials that are resistant to water damage. Permeable surfaces, such as porous pavement, can also be used to help manage storm water runoff and reduce the risk of flooding in urban areas.
Cool Pavements and Surfaces
Cool pavements and surfaces are designed to reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat than conventional materials, such as asphalt. This can help to reduce the urban heat island effect, which occurs when built-up areas become significantly warmer than their rural surroundings due to the absorption and re-radiation of heat by buildings and pavements. By mitigating the urban heat island effect, cool pavements can improve air quality, reduce energy consumption, and enhance the comfort and health of urban residents.
Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design uses the sun’s energy to heat, cool, and light buildings without the need for mechanical systems. By taking advantage of natural ventilation, thermal mass, and solar orientation, passive solar design can significantly reduce the energy consumption and environmental impacts of buildings. Some key principles of passive solar design include maximizing south-facing windows, using thermal mass to store heat, and providing effective shading and insulation.
Modular and Prefabricated Construction
Modular and prefabricated construction techniques involve assembling buildings from pre-made components, which can be manufactured off-site and transported to the construction site for assembly. This approach can reduce waste, minimize disruption to the local environment, and allow for faster and more efficient construction. In addition, modular and prefabricated buildings can be designed to be more resilient to extreme weather events and natural disasters.
Conclusion
Building resilient cities is essential for protecting our urban environments and their inhabitants from the impacts of climate change. By adopting innovative climate-adaptive construction techniques, we can create buildings and infrastructure that are more resilient, sustainable, and adaptable to changing environmental conditions. By working together, urban planners, architects, engineers, and policymakers can help to ensure that our cities are better prepared for the challenges of the future.